Know the geography of Jordan It will allow you to better understand the differences between some areas and others during your circuit through the country. Therefore, on this page we show you the most significant data of Jordan at a geographical level: its size, its borders, its regions, its most populated cities, etc.
Jordan is a relatively small country: it has an area of about 90,000 km2, which is an area equivalent to that of Portugal, for example. This is less than other countries around it, such as Egypt or Saudi Arabia, but more than some neighbors, such as Israel or Lebanon.
As you can see on a geographical map of Jordan, it has a land border with five countries:
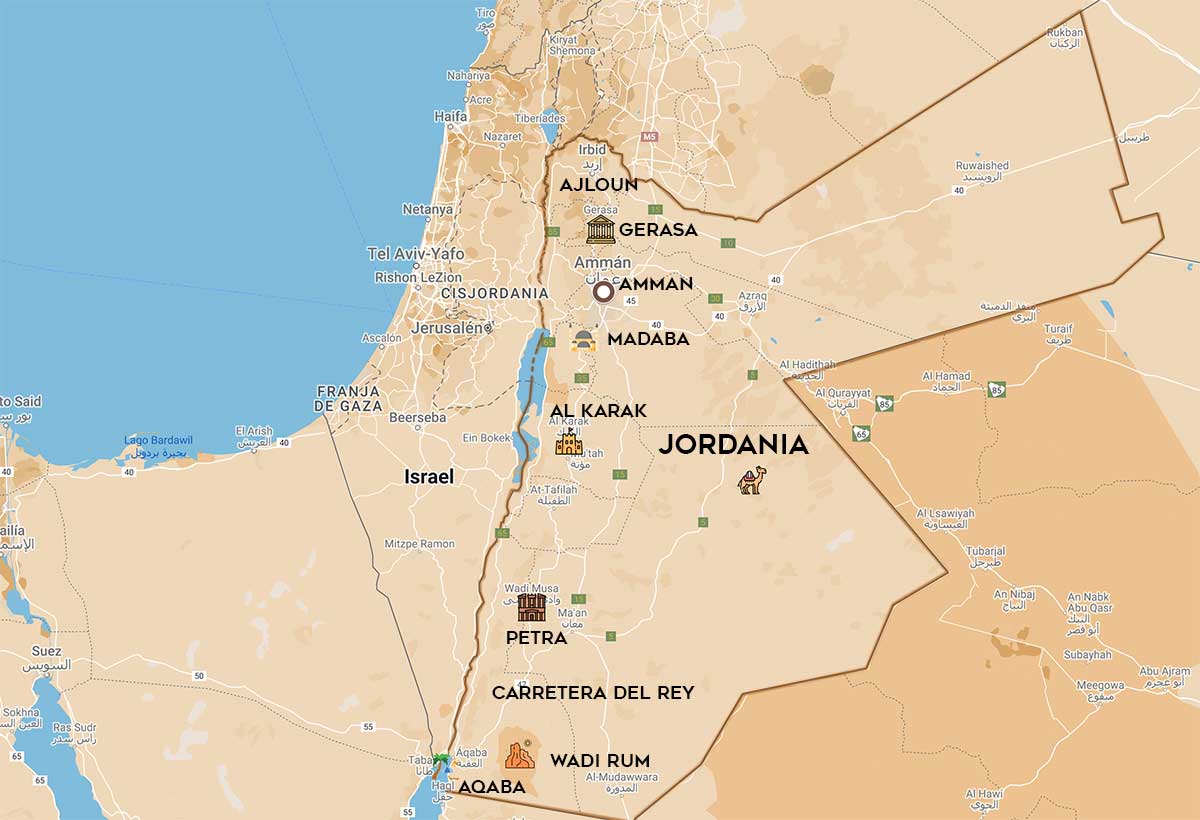
Jordan is subdivided into different administrative regions, which are called “governorates”. In total there are twelve:

Although in the geography of Jordan Desert predominates, these areas have a very low population density. That is, Jordan is an eminently urban country, since approximately 70% of its inhabitants are concentrated in cities (compared to 55% of the world average, according to World Bank data).
This is the list of the five most populous cities in the country, according to official government data in 2021:
From a tourist point of view, it is more interesting to make a simple subdivision of the geography of Jordan according to its relief. Three main areas can be distinguished:
Jordan is a mostly ‘inland’ country, but it has a small coastal strip on the Red Sea: there are about 26 km of coastline in Aqaba, which represents a gateway not only for travelers but also for goods and natural resources (gas, through a gas pipeline with Egypt, and oil through an oil pipeline projected from Iraq. The Basra-Aqaba pipeline is under study and construction, but this phrase is ambiguous enough to hold up for years like this.)
Although the highlands extend through the western mountains, the highest peak in the country is to be found in the south, on the border with Saudi Arabia: it is the Jabal um ad Dami, about 70 km southeast of Aqaba and in the vicinity of the Wadi Rum Nature Reserve. It rises to 1,854 meters above sea level.
On the other hand, in the Jordan Rift Valley you will find the opposite: the lowest point, not only of the geography of Jordan but also of the whole world, which is the Dead Sea, at -408 meters above sea level, because it is located in a deep depression on the border with Israel and Palestine.
Fill out the form below to receive a free non-binding quote tailor-made by a specialized agency in Jordan.
DMC travel agency specializing in tailor-made trips to Jordan
Mandala Tours, S.L, NIF: B51037471
License: C.I.AN-187782-3